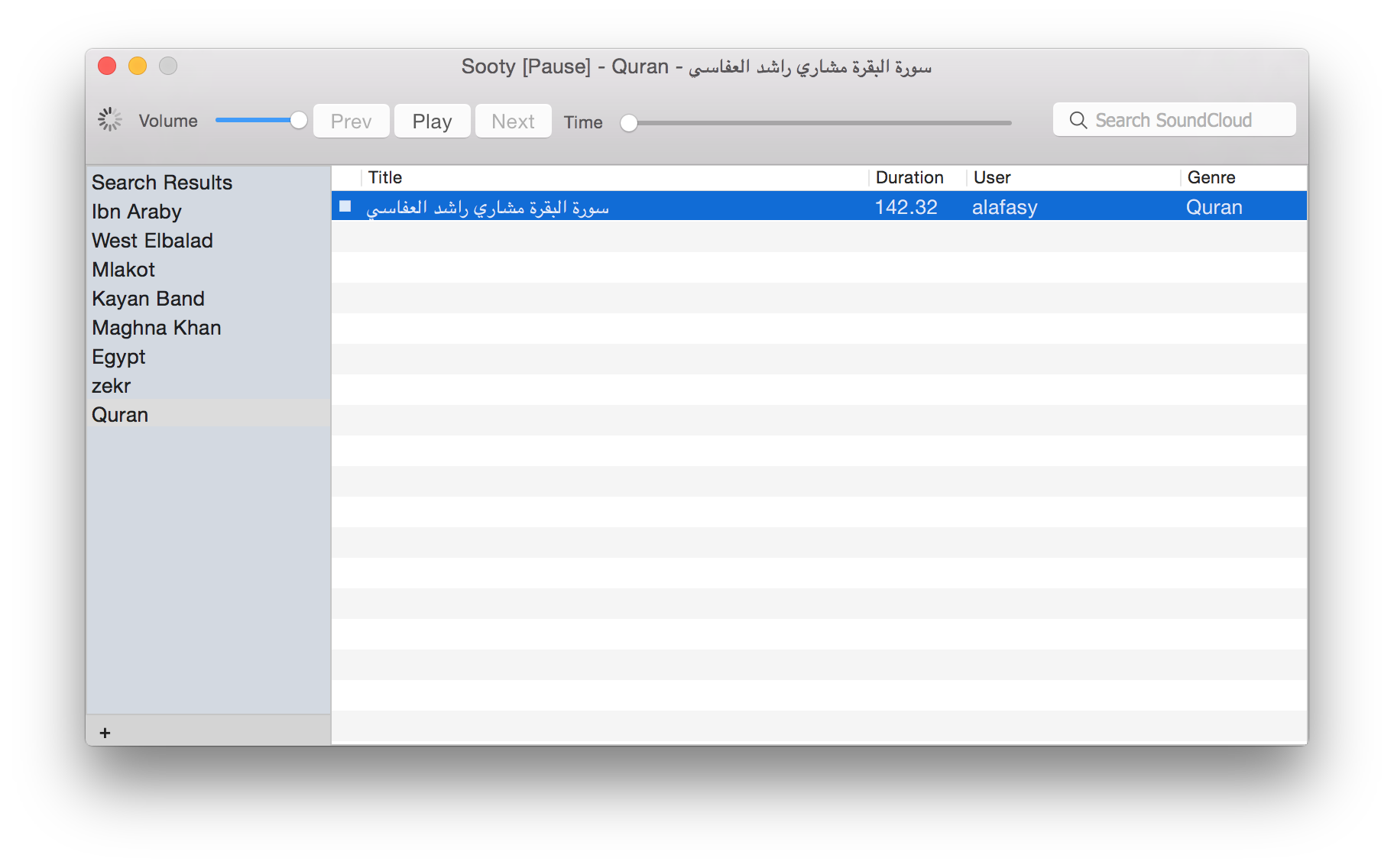
I did some project to play sounds directly from soundcloud few months ago...
I share it here .. the URL of the dmg file: https://github.com/MuhammadHewedy/Sooty/releases
Source code: https://github.com/MuhammadHewedy/Sooty

// NSObject+TurnLights.h
// a Category on NSObject to allow any subclass to turn on/off lights
@interface NSObject (TurnLights)
-(void) turnLightsOn;
-(void) turnLightsOff;
@end
//Lights.m
// this is the lights class that delegate its work to some object (of type id) to do the on/off instead of itself
@implementation Lights
@synthesize id delegate;
-(void) doLightings{
[delegate turnLightsOn];
[delegate turnLightsOff];
}
@end
//MyContorller.m
// is my controller class that decided to be a delegate for the Lights class
#import "NSObject+TurnLights.h"
@implementation MyController
-(void) btnClicked:(id) sender{
Lights* lights = ...
[lights setDelegate: self];
}
-(void) turnLightsOn{
NSLog("turnLightsOn");
}
-(void) turnLightsOff{
NSLog("turnLightsOff");
}
@end
CellIdentifier = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"cell%@", @"some_term_per_page"];
cell = [_tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:CellIdentifier];
if (cell == nil)
{
cell = [[[UITableViewCell alloc] initWithStyle:UITableViewCellStyleSubtitle reuseIdentifier:CellIdentifier] autorelease];
}
SomeData* data = [self data:indexPath.row];
if ([[cell.contentView subviews] count] > 0)
[[[cell.contentView subviews]objectAtIndex:0]removeFromSuperview];
[cell.contentView addSubview:[DrawingHelper cellView:data]];
1. 2. #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> 3. 4. @interface URLCaller : NSObject 5. { 6. NSMutableData* data; 7. NSObject* target; 8. SEL selector; 9. } 10. @property (nonatomic, retain) NSMutableData* data; 11. @property (nonatomic, retain) NSObject* target; 12. @property (nonatomic) SEL selector; 13. 14. -(id) initWithTarget:(NSObject*) target selector:(SEL)selector; 15. -(void) call:(NSString*) url; 16. 17. @end 18. 19. 20. #import "URLCaller.h" 21. 22. @implementation URLCaller 23. @synthesize data, target, selector; 24. 25. -(id) initWithTarget:(NSObject*) _target selector:(SEL)_selector 26. { 27. if (self = [super init]) 28. { 29. self.target = _target; 30. self.selector = _selector; 31. } 32. return self; 33. } 34. 35. -(void) call:(NSString*) url 36. { 37. NSURLConnection* connection = [[NSURLConnection alloc]initWithRequest:[NSURLRequest requestWithURL:[NSURL URLWithString:url]] delegate:self]; 38. [connection release]; 39. } 40. 41. #pragma mark - NSURLConnection deleages 42. 43. -(void)connection:(NSURLConnection*)connection didReceiveResponse:(NSURLResponse*)response 44. { 45. data = [[NSMutableData alloc] init]; // _data being an ivar 46. } 47. -(void)connection:(NSURLConnection*)connection didReceiveData:(NSData*)_data 48. { 49. [self.data appendData:_data]; 50. } 51. -(void)connection:(NSURLConnection*)connection didFailWithError:(NSError*)error 52. { 53. // Handle the error properly 54. } 55. -(void)connectionDidFinishLoading:(NSURLConnection*)connection 56. { 57. NSString* stringData = [[[NSString alloc]initWithData:data encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]autorelease]; 58. [target performSelector:selector withObject:stringData]; 59. } 60. 61. - (void)dealloc 62. { 63. [target release]; 64. [data release]; 65. [super dealloc]; 66. } 67. 68. @endAnd in the caller class (in my case is a ViewController), we will use the URLCaller class:
1. 2. -(IBAction)getDataFromServer:(id)sender 3. { 4. URLCaller* caller = [[URLCaller alloc]initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(setTextViewContents:)]; 5. [caller call:@"http://search.twitter.com/search.json?q=Muhammad"]; 6. [caller release]; 7. } 8. 9. // this will got called when the data returned from the server 10. -(void) setTextViewContents:(NSString*) contents 11. { 12. text.text = contents; 13. }You can get the project source code from here Very important notice is that, the application will never got freeze while the data is being transferred, and this is what we wants!
NSJSONSerialization.h, NSJSONSerialization.m and GSFastEnumeration.h, although not worked directly, I've did very small modifications
~/objc/json
cd ~/objc/json and issue the following command to build the files:
gcc -c `gnustep-config --objc-flags` *.m
NSJSONSerialization.h and GSFastEnumeration.h to /GNUstep/System/Library/Headers/Foundation ar q libNSJSONSerialization.a NSJSONSerialization.o
Then move the generated libNSJSONSerialization.a file to /GNUstep/System/Library/Libraries/
~/objc/json and all of its contents.
NSJSONSerialization as a static lib into gnustep.~/objc/json_test and create a file named json_main.m in this directory.1. #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> 2. #import <Foundation/NSJSONSerialization.h> 3. 4. int main(void) 5. { 6. NSAutoreleasePool* pool = [[NSAutoreleasePool alloc]init]; 7. 8. NSDictionary* dictionary = [NSDictionary dictionaryWithObjects: 9. [NSArray arrayWithObjects: @"Muhammad", @"26", @"2011", @"Cairo, Egypt", 10. [NSArray arrayWithObjects: @"Arabic", @"English", nil] , nil] 11. forKeys: 12. [NSArray arrayWithObjects: @"name", @"age", @"year", @"address", @"language", nil]]; 13. NSError* error; 14. NSData* data = [NSJSONSerialization dataWithJSONObject: dictionary 15. options:NSJSONWritingPrettyPrinted 16. error: &error]; 17. if (error) 18. { 19. NSLog(@"ERROR %@", error); 20. }else 21. { 22. NSString* jsonString = [[NSString alloc] initWithData: data 23. encoding: NSASCIIStringEncoding]; 24. NSLog(@"%@", jsonString); 25. 26. [jsonString release]; 27. } 28. 29. [pool release]; 30. return 0; 31. }Now use the following command to compile it:
gcc `gnustep-config --objc-flags` *.m -L /GNUstep/System/Library/Libraries -lNSJSONSerialization -lobjc -lgnustep-base
$ a.exe
2011-09-18 01:35:49.726 a[5696] {
"language": [
"Arabic",
"English"
],
"year": "2011",
"name": "Muhammad",
"age": "26",
"address": "Cairo, Egypt"
}
1. #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> 2. 3. int main(void) 4. { 5. 6. NSAutoreleasePool* pool = [NSAutoreleasePool new]; 7. 8. typedef struct 9. { 10. char* name; 11. int hiredate; 12. }Emp; 13. 14. Emp emps[] = {{"Mouhammad", 2010}, {"Moutaz", 2010}, {"Ahmad", 2010}}; 15. 16. NSData* data = [NSData dataWithBytes : emps length: sizeof(Emp) * 3 ]; // here we specify the number of BYTES to be holded 17. 18. Emp* newEmps = [data bytes]; 19. int count = [data length]/ sizeof(Emp); // here we go the number of bytes holded, 20. //watch the division of the total number of bytes 21. // over the size of each struct element 22. 23. int i=0; 24. for (; i< count; i++) 25. { 26. Emp e = *newEmps; 27. NSLog(@"%s %i", e.name, e.hiredate); 28. newEmps++; 29. } 30. 31. 32. [pool release]; 33. return 0; 34. }
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h> #import "../../mem.h" @interface NSDate(description) -(NSString*) description; @end @implementation NSData(description) -(NSString*) description { int len = [self length]; char buff[len]; [self getBytes: buff]; NSMutableString* ret = [NSMutableString string]; int i; for (i=0; i < len; i++) [ret appendFormat: @"%i ", buff[i] ]; return ret; } @end int main(void) { POOL; char arr[]= {10, 20, 30}; NSData* data = [NSData dataWithBytes:arr length: sizeof(arr)/sizeof(char)]; NSLog(@"%@", [data description]); _POOL; return 0; }Note, POOL and _POOL are two macros defined in "../../mem.h" as follow: #define POOL NSAutoreleasePool* pool = [[NSAutoreleasePool alloc] init] #define _POOL [pool drain]
1. typedef struct 2. { 3. char* name; 4. }Emp;I asked in SO on how to determine the amount of memory to allocate to the char* struct member. and the answer was to use lazy/delayed allocation as of:
1. void setName(Emp* emp, char* newName) 2. { 3. free(emp->name); 4. emp->name = malloc(strlen(newName) + 1); 5. strcpy(emp->name, newName); 6. }(It seems to me to be the same idea used for Objective-C, the setter is release the previous pointer and then retain (in C to copy) the parameter pointer. So, the whole program will be:
1. #include <stdio.h> 2. #include <string.h> 3. #include <stdlib.h> 4. 5. typedef struct 6. { 7. char* name; 8. }Emp; 9. 10. void init(Emp** emp) 11. { 12. *emp = malloc(sizeof(Emp)); 13. (*emp)->name = NULL; 14. (*emp)->name = malloc(sizeof(char*)); 15. } 16. 17. void release(Emp** emp) 18. { 19. free((*emp)->name); 20. free(*emp); 21. } 22. 23. void setName(Emp* emp, char* newName) 24. { 25. free(emp->name); 26. emp->name = malloc(strlen(newName) + 1); 27. strcpy(emp->name, newName); 28. } 29. char* getName(Emp* emp) 30. { 31. return emp->name; 32. } 33. 34. int main(void) 35. { 36. Emp* emp; 37. init(&emp); 38. setName(emp, "Muhammad Abdullah"); 39. printf("%s", getName(emp)); 40. release(&emp); 41. 42. return 0; 43. }
1. #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> 2. 3. int main(void) 4. { 5. long long i; 6. for (i=0; i < 100000000000000; i++) 7. { 8. NSString* string = [[NSString alloc] initWithString :@"string"]; 9. //[string release]; 10. } 11. 12. [NSThread sleepForTimeInterval: 5]; 13. 14. return 0; 15. }Then compile and run with GNUstep, the memory used by the program reaches 2 GB (I've 4 GB of RAM), and then the program terminates printing:
Virtual memory exhausted This application has requested the Runtime to terminate it in an unusual way. Please contact the application's support team for more information.Remember, each time you enter a block of code (method for example) and allocate the miss to deallocate the memory you allocate will add this to the RAM and will not remove..finally you may find your program get crashed because it uses too much memory !
1. //string_2_primtiives.m 2. #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> 3. 4. /** 5. * You can convert the following to each other 6. * NSNumber <=> primitives <=> NSString 7. */ 8. 9. int main(void) 10. { 11. NSAutoreleasePool* pool = [[NSAutoreleasePool alloc] init]; 12. 13. //1- primitives => NSNumber 14. NSNumber* intNum = [NSNumber numberWithInteger: 20]; 15. NSNumber* floatNum = [NSNumber numberWithFloat: 25.325]; 16. 17. NSLog(@"%@ %@", intNum, floatNum); 18. 19. // 2- NSNumber => primitives: 20. int x = [intNum intValue]; 21. float f = [floatNum floatValue]; 22. // also, we can convert nay number object (regards of which value it contains) to any primitives type 23. //, and the standard C casting rules will be applied: 24. int x2 = [floatNum intValue]; 25. 26. NSLog(@"%d %g %d", x, f, x2); 27. 28. // 3- primitives => NSString: 29. NSString* string = [NSString stringWithFormat: @"%d",x]; 30. NSLog(@"%@", string); 31. 32. // 4- NSString = > primitives: 33. int i = [@"1" intValue]; 34. float g = [@"13.4" floatValue]; 35. int i2 = [@"13.4" intValue]; 36. 37. NSLog(@"%d %g %d", i, g, i2); 38. 39. // 5- NSNumber => NSString 40. NSString* str = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@", [NSNumber numberWithBool:20]]; 41. NSLog(@"%@", str); 42. 43. // 6- NSString => NSNumber 44. NSNumber* charNum = [NSNumber numberWithChar: [@"20" intValue]]; 45. NSLog(@"%@", charNum); 46. 47. [pool release]; 48. return 0; 49. } 50. 51. /** output: 52. 53. 20 25.325 54. 20 25.325 25 55. 20 56. 1 13.4 13 57. 1 58. 20 59. 60. */
1. 2. public class Abc 3. { 4. public static void main(String[] args) 5. { 6. B.func(); 7. // 1- B will inherit `func() from A. 8. // 2- `func()` call the method `x()` 9. // 3- since `func()` is a static method in Class A, it will reference non-qualified methods as static methods in the same class 10. // 4- `func()` will call `x()` from the same class it resids in (class A) 11. } 12. } 13. 14. class A 15. { 16. static void x() 17. { 18. System.out.println("in A"); 19. 20. } 21. 22. static void func() 23. { 24. x(); // as if we call : A.x(); 25. } 26. } 27. 28. class B extends A 29. { 30. static void x() 31. { 32. System.out.println("in B"); 33. 34. } 35. }
1. //A.h 2. #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> 3. 4. @interface A : NSObject 5. 6. +(void) x; 7. +(void) func; 8. 9. @end 10. 11. @implementation A 12. +(void) x 13. { 14. NSLog(@"in A"); 15. } 16. +(void) func 17. { 18. [self x]; 19. } 20. 21. @end
1. //B.h 2. #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> 3. #import "A.h" 4. 5. @interface B : A 6. 7. +(void) x; 8. 9. @end 10. 11. @implementation B 12. 13. +(void) x 14. { 15. NSLog(@"in B"); 16. } 17. 18. @end
1. //Main.m 2. #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> 3. #import "B.h" 4. 5. int main(void) 6. { 7. 8. [B func]; 9. 10. return 0; 11. }
mingw-get install mintty
C:\GNUstep\msys\1.0\bin\mintty.exe /bin/env CHERE_INVOKING=1 /bin/bash -l
cat <<EOF>hello.c
#include<stdio.h>
int main(void){printf("In the name of Allah\n");}
EOF
gcc -o hello hello.c && ./hello
In the name of Allah
//Point.h #import <objc/Object.h> @interface Point : Object { @private double x; double y; } -(id) x: (double) x_value; -(double) x; -(id) y: (double) y_value; -(double) y; -(double) magnitude; @end
//Point.m #import "Point.h" #import <math.h> @implementation Point -(id) x: (double) x_value { x = x_value; return self; } -(double) x { return x; } -(id) y: (double) y_value { y = y_value; return self; } -(double) y { return y; } -(double) magnitude { return sqrt(x*x + y*y); } @end
//Test.m #import "Point.h" #import <stdio.h> int main(void) { Point *p = [[Point alloc] init]; [p x:10.0]; [p y:20.0]; printf("The Distance from Point %g to %g is %g\n", [p x], [p y], [p magnitude]); return 0; }
gcc -o Test *.m -lobjc -lm
./Test
The Distance from Point 10 to 20 is 22.3607